Gramatica a reflexive verbs answers provides a comprehensive exploration of reflexive verbs, their conjugation, usage, and common mistakes. This guide delves into the intricacies of reflexive verbs, offering clear explanations and practical examples to enhance understanding.
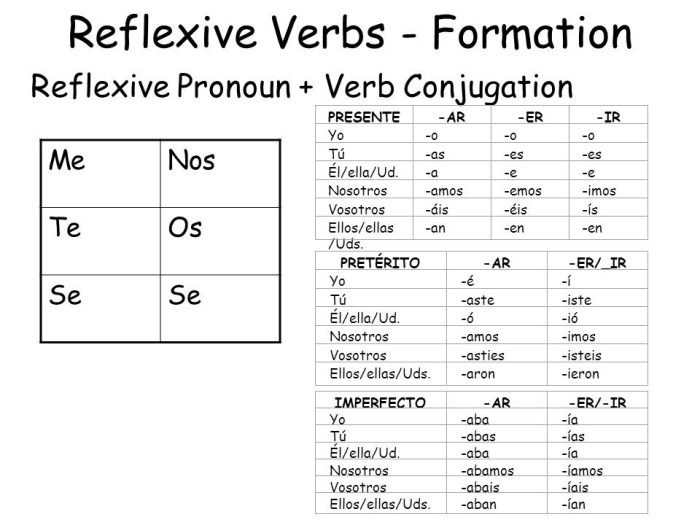
This guide covers the definition of reflexive verbs, explaining the concept of the subject and object being the same entity. It explores the general rules for conjugating reflexive verbs and provides a table illustrating their conjugation in different tenses and persons.
Additionally, it discusses the usage of reflexive verbs in various contexts, highlighting the different meanings they convey.
Definition of Reflexive Verbs

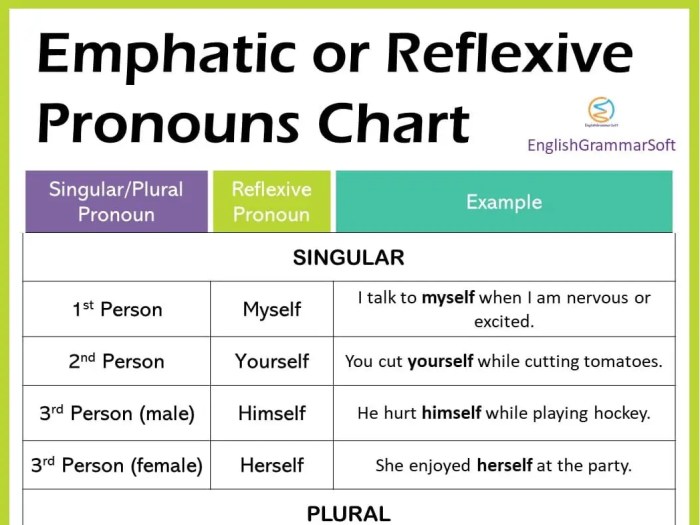
In grammar, a reflexive verb is a verb that requires a reflexive pronoun as its object. Reflexive pronouns are pronouns that refer back to the subject of the verb. For example, in the sentence “I washed myself,” the reflexive pronoun “myself” refers back to the subject “I.”
Reflexive verbs are used to indicate that the subject of the verb is performing an action on itself.
Reflexive verbs are common in many languages, including English. Some of the most common reflexive verbs in English include “wash,” “dress,” “shave,” and “bathe.”
Identifying Reflexive Verbs
There are a few key ways to identify reflexive verbs. First, reflexive verbs always have a reflexive pronoun as their object. Second, the subject and object of a reflexive verb are always the same entity. Third, reflexive verbs are often used to indicate that the subject of the verb is performing an action on itself.
Conjugation of Reflexive Verbs: Gramatica A Reflexive Verbs Answers
Conjugating reflexive verbs in Spanish follows specific rules. Understanding these rules is essential for accurate usage in different tenses and persons.
The general rule for conjugating reflexive verbs is to add the reflexive pronoun to the infinitive form of the verb and then conjugate it according to the tense and person.
Tense Conjugation
| Tense | Person | Conjugation |
|---|---|---|
| Present | Yo | me (yo) |
| Tú | te (tú) | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | se (él/ella/usted) | |
| Nosotros | nos (nosotros) | |
| Vosotros | os (vosotros) | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | se (ellos/ellas/ustedes) | |
| Preterite | Yo | me (yo) |
| Tú | te (tú) | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | se (él/ella/usted) | |
| Nosotros | nos (nosotros) | |
| Vosotros | os (vosotros) | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | se (ellos/ellas/ustedes) | |
| Imperfect | Yo | me (yo) |
| Tú | te (tú) | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | se (él/ella/usted) | |
| Nosotros | nos (nosotros) | |
| Vosotros | os (vosotros) | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | se (ellos/ellas/ustedes) | |
| Future | Yo | me (yo) |
| Tú | te (tú) | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | se (él/ella/usted) | |
| Nosotros | nos (nosotros) | |
| Vosotros | os (vosotros) | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | se (ellos/ellas/ustedes) | |
| Conditional | Yo | me (yo) |
| Tú | te (tú) | |
| Él/Ella/Usted | se (él/ella/usted) | |
| Nosotros | nos (nosotros) | |
| Vosotros | os (vosotros) | |
| Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes | se (ellos/ellas/ustedes) |
Irregularities and Exceptions
There are a few irregularities and exceptions in the conjugation of reflexive verbs. For example, in the present tense, the verb “irse” (to go away) conjugates as “me voy,” “te vas,” “se va,” etc., instead of “me iré,” “te irás,” “se irá,” etc.
Usage of Reflexive Verbs
Reflexive verbs are a type of verb that indicates that the action is performed by and to the same person or thing. They are commonly used in a variety of contexts to express different meanings, including:
- Personal hygiene:Reflexive verbs are often used to describe actions related to personal hygiene, such as washing, dressing, and grooming.
- Mental and emotional states:Reflexive verbs can also be used to express mental and emotional states, such as feeling happy, sad, or angry.
- Physical actions:Reflexive verbs can be used to describe physical actions that are performed on oneself, such as stretching, bending, and turning.
- Idiomatic expressions:Reflexive verbs are also used in a variety of idiomatic expressions, such as “to make oneself at home” and “to take care of oneself.”
Here are some examples of reflexive verbs in sentences:
- I washed myselfin the shower.
- She felt herselfgetting angry.
- The cat stretched itselfout on the couch.
- Please make yourselfat home.
Comparison with Non-Reflexive Verbs
Reflexive verbs differ from non-reflexive verbs in their usage and the subtle nuances they convey. Understanding these differences is crucial for accurate and effective communication in the target language.
Usage
Non-reflexive verbs are employed when the subject of the verb is not also the recipient of the action. For instance, “I eat” implies that the speaker is consuming food, but the action is not directed towards themselves. In contrast, reflexive verbs are utilized when the subject and the recipient of the action are the same.
For example, “I wash myself” indicates that the speaker is performing the action of washing upon themselves.
Meaning and Emphasis
The use of reflexive verbs often emphasizes the subject’s involvement in the action. By employing a reflexive pronoun, the speaker highlights that the action is being performed by and upon the subject. This emphasis can convey a sense of self-care, responsibility, or reciprocity.
For instance, “I dressed myself” implies that the speaker took the initiative to put on their clothes, while “I dressed” could suggest that someone else assisted them.
Examples
The following table illustrates the differences between reflexive and non-reflexive verbs:
| Non-Reflexive Verb | Reflexive Verb | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| I wash | I wash myself | I clean myself |
| I dress | I dress myself | I put on my clothes |
| I eat | I feed myself | I provide myself with food |
Common Mistakes and Corrections
When using reflexive verbs, learners often make certain mistakes. These mistakes can stem from various factors, such as confusion with non-reflexive verbs or a lack of understanding of the reflexive pronoun’s function.
To avoid these mistakes, it is essential to grasp the fundamental rules and nuances of reflexive verb usage. This section will highlight common errors and provide corrections to enhance your comprehension and proficiency in using reflexive verbs.
Mistaking Reflexive for Non-Reflexive Verbs
One common error is using reflexive verbs in situations where non-reflexive verbs are appropriate. This mistake typically occurs when learners are unfamiliar with the specific reflexive verbs and their corresponding non-reflexive counterparts.
For example, the verb “lavar” (to wash) is non-reflexive, meaning it does not require a reflexive pronoun. However, some learners may mistakenly use the reflexive form “lavarse” (to wash oneself) even when referring to washing an object or another person.
To avoid this mistake, it is crucial to memorize the correct reflexive verbs and their non-reflexive equivalents. Additionally, paying attention to the context and the intended meaning of the sentence will help you choose the appropriate verb form.
Incorrect Use of Reflexive Pronouns
Another common mistake is using incorrect reflexive pronouns. Reflexive pronouns must agree in number and person with the subject of the verb. For example, the reflexive pronoun “me” is used for the first person singular subject, while “nos” is used for the first person plural subject.
Incorrect use of reflexive pronouns can lead to confusion and make the sentence grammatically incorrect. For instance, saying “Yo me lavo el coche” (I wash the car myself) is incorrect because the reflexive pronoun “me” does not match the subject “yo” (I), which requires the reflexive pronoun “me”.
The correct sentence should be “Yo me lavo el coche” (I wash the car myself).
To avoid this mistake, always ensure that the reflexive pronoun matches the subject of the verb in number and person. Refer to the table of reflexive pronouns for guidance.
Omitting Reflexive Pronouns, Gramatica a reflexive verbs answers
In some cases, learners may omit the reflexive pronoun altogether, which is incorrect. Reflexive pronouns are essential for indicating that the action of the verb is directed back to the subject. Without the reflexive pronoun, the sentence may lose its intended meaning or become grammatically incorrect.
For example, the sentence “Me ducho todas las mañanas” (I shower every morning) is correct because the reflexive pronoun “me” indicates that the action of showering is performed by the subject “yo” (I). If the reflexive pronoun were omitted, the sentence would become “Ducho todas las mañanas”, which is grammatically incorrect.
To avoid this mistake, always include the appropriate reflexive pronoun when using reflexive verbs. Remember that reflexive pronouns are essential for conveying the reflexive nature of the action.
Using Reflexive Verbs for Non-Reflexive Actions
Another mistake to avoid is using reflexive verbs for actions that are not reflexive. Reflexive verbs are specifically used to indicate that the action of the verb is directed back to the subject. Using them for non-reflexive actions can lead to confusion or incorrect sentence structure.
For example, the verb “comer” (to eat) is non-reflexive, meaning it does not require a reflexive pronoun. However, some learners may mistakenly use the reflexive form “comerse” (to eat oneself) even when referring to eating food. This is incorrect because the action of eating is not directed back to the subject.
To avoid this mistake, carefully consider the meaning of the verb and the intended action. Use reflexive verbs only when the action is genuinely reflexive, meaning it is directed back to the subject.
Query Resolution
What are reflexive verbs?
Reflexive verbs are verbs where the subject and object are the same entity.
How are reflexive verbs conjugated?
Reflexive verbs are conjugated by adding the reflexive pronoun to the infinitive form of the verb.
When are reflexive verbs used?
Reflexive verbs are used to indicate that the action of the verb is being performed on the subject by itself.
What are some common mistakes made with reflexive verbs?
Common mistakes include using the wrong reflexive pronoun or forgetting to use the reflexive pronoun altogether.