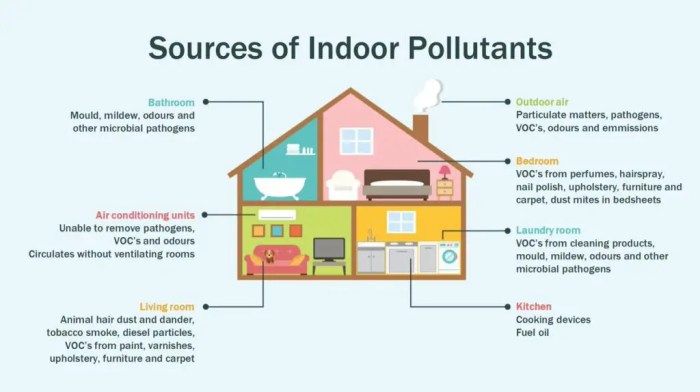
Which correctly pairs an indoor pollutant with its source? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of indoor air pollution, exploring common pollutants, their potential health effects, and the primary sources responsible for their presence. By understanding these connections, we empower ourselves to create healthier and more comfortable indoor environments.
Indoor air pollution poses significant health risks, ranging from short-term discomfort to long-term respiratory and cardiovascular issues. Identifying the sources of these pollutants is crucial for developing effective strategies to mitigate their impact.
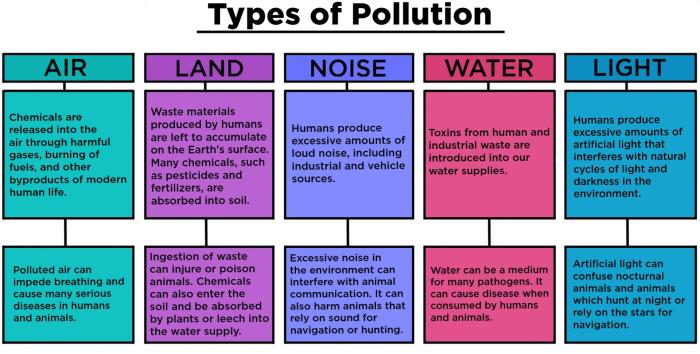
Indoor Pollutants and Sources
Indoor air pollution is a significant environmental health concern, as people spend a considerable amount of time indoors. Common indoor pollutants include:
- Volatile organic compounds (VOCs): Emitted from paints, cleaning products, and building materials, VOCs can cause respiratory irritation, headaches, and nausea.
- Particulate matter (PM): Fine particles suspended in the air, PM can be inhaled deeply into the lungs, leading to respiratory and cardiovascular problems.
- Carbon monoxide (CO): A colorless, odorless gas produced by combustion appliances, CO can cause dizziness, headaches, and even death in high concentrations.
- Formaldehyde: A chemical used in building materials and furniture, formaldehyde can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat.
- Radon: A radioactive gas that occurs naturally in the soil, radon can increase the risk of lung cancer.
Ventilation and Pollutant Reduction, Which correctly pairs an indoor pollutant with its source
Ventilation is crucial for reducing indoor air pollution by diluting and removing pollutants. Different ventilation systems can affect pollutant levels:
- Natural ventilation: Opening windows and doors allows fresh air to enter and circulate.
- Mechanical ventilation: Using fans or air conditioning units to circulate air and exhaust pollutants.
- Balanced ventilation: A combination of natural and mechanical ventilation, ensuring a constant supply of fresh air while removing pollutants.
Improving ventilation involves:
- Increasing natural ventilation by opening windows and doors.
- Using exhaust fans in kitchens and bathrooms to remove pollutants.
- Installing balanced ventilation systems for efficient air exchange.
Essential FAQs: Which Correctly Pairs An Indoor Pollutant With Its Source
What are the most common indoor pollutants?
Common indoor pollutants include particulate matter, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), carbon monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and formaldehyde.
How can I reduce indoor air pollution?
Improving ventilation, using air purifiers, and reducing sources of pollution can effectively reduce indoor air pollution levels.
What are the health effects of indoor air pollution?
Exposure to indoor air pollution can cause a range of health problems, including respiratory issues, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.