Organelles and illness activity answers are intricately intertwined, providing a comprehensive understanding of how cellular dysfunction can lead to a myriad of diseases. This article delves into the multifaceted roles of organelles, their impact on cellular processes, and their potential as therapeutic targets.
From the powerhouse mitochondria to the protein-synthesizing ribosomes, organelles are the building blocks of life, performing essential functions that sustain cellular health. However, when these organelles malfunction, they can trigger a cascade of events that disrupt cellular homeostasis, leading to the development of various illnesses.
Organelles and their Functions: Organelles And Illness Activity Answers
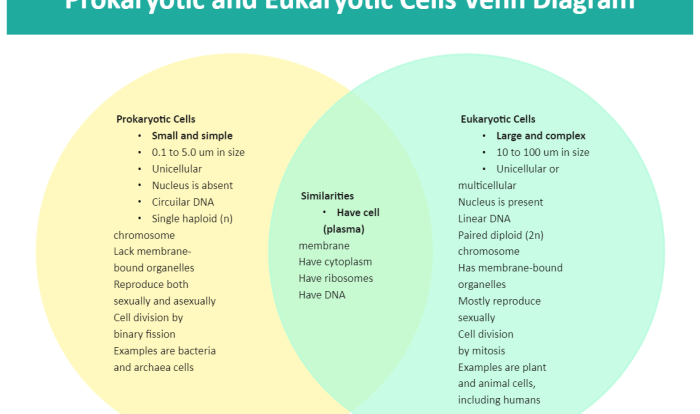
Organelles are specialized structures found within eukaryotic cells that perform specific functions essential for cell survival and operation. Each organelle has a distinct structure and function, working together to maintain cellular homeostasis and perform various biochemical processes.
List of Organelles and their Functions, Organelles and illness activity answers
- Nucleus:Control center of the cell, housing the genetic material (DNA) and regulating cellular activities.
- Mitochondria:Energy powerhouses, producing ATP through cellular respiration.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER):Involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.
- Golgi Apparatus:Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion.
- Lysosomes:Contain digestive enzymes for breaking down waste materials and cellular debris.
- Peroxisomes:Detoxify harmful substances and play a role in lipid metabolism.
- Ribosomes:Protein synthesis machinery, translating mRNA into proteins.
- Cytoskeleton:Network of filaments and tubules providing structural support and facilitating cell movement.
- Centrosome:Organizes microtubules and initiates cell division.
- Vacuoles:Storage compartments for various substances, including water, ions, and waste products.
Quick FAQs
What are the most common organelles associated with disease?
Mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and lysosomes are among the organelles most frequently implicated in disease.
How can organelle dysfunction contribute to disease development?
Organelle dysfunction can disrupt cellular processes, leading to the accumulation of toxic substances, impaired energy production, and protein misfolding, which can ultimately trigger disease.
What are some examples of diseases associated with organelle dysfunction?
Mitochondrial disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease, are caused by mitochondrial dysfunction. Cystic fibrosis and lysosomal storage diseases are examples of illnesses linked to dysfunction of the endoplasmic reticulum and lysosomes, respectively.