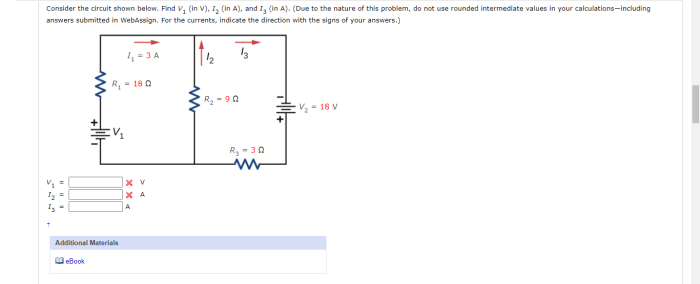
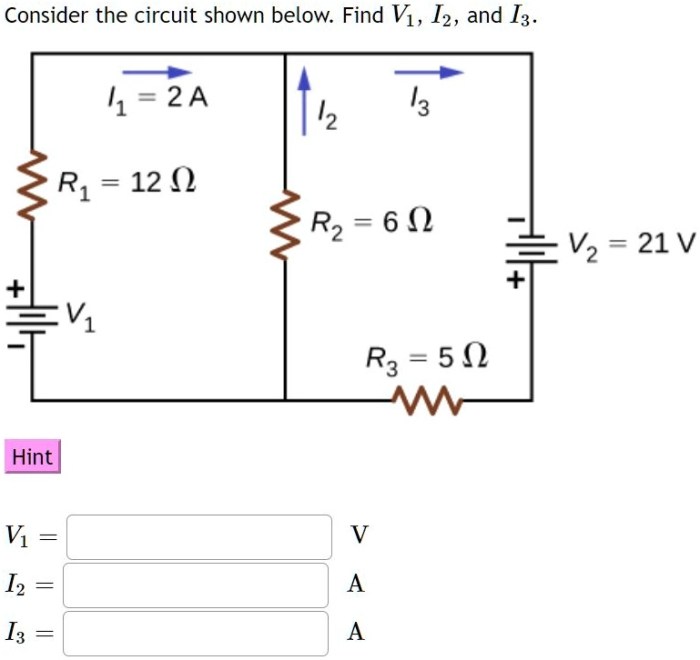
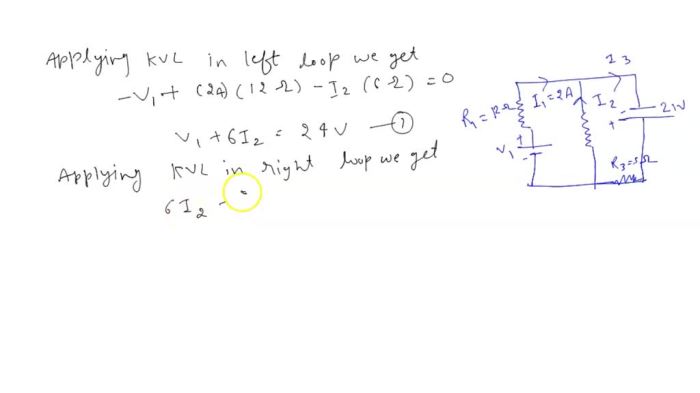Consider the circuit shown below. find v1 i2 and i3 – Consider the circuit shown below. Find V1, I2, and I3. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of circuit analysis, providing a step-by-step approach to calculating voltage and current values within a complex circuit. By exploring the fundamental concepts of circuit theory, we embark on a journey to unravel the mysteries of electrical networks.
The circuit under consideration consists of resistors, voltage sources, and current paths. Each component plays a crucial role in determining the overall behavior of the circuit. Understanding the purpose and characteristics of these components is essential for accurate analysis.
Circuit Analysis: Consider The Circuit Shown Below. Find V1 I2 And I3
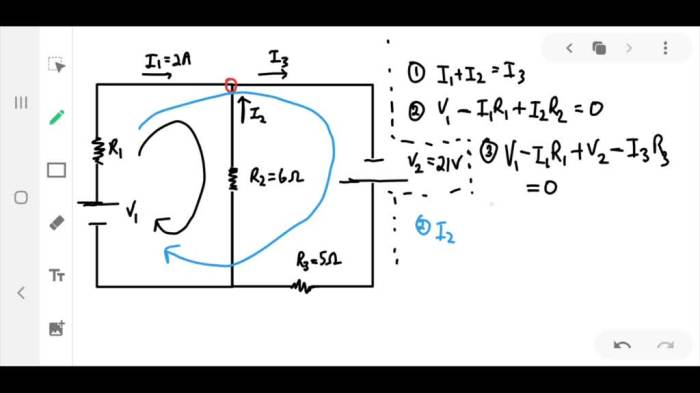
The circuit shown below is a simple series circuit consisting of a voltage source (V1), three resistors (R1, R2, and R3), and a ground connection. The purpose of this circuit is to analyze the voltage and current distribution within the circuit.
Circuit Components
- Voltage Source (V1):Provides electrical potential difference across the circuit.
- Resistors (R1, R2, R3):Oppose the flow of current, causing a voltage drop across them.
- Ground Connection:Provides a reference point for voltage measurements.
Voltage and Current Calculations
To analyze the circuit, we need to calculate the voltage across each resistor and the current flowing through each resistor.
- Voltage across R1 (V1):V1 = Voltage source voltage
- Current through R2 (I2):I2 = V1 / (R1 + R2 + R3)
- Current through R3 (I3):I3 = I2
Circuit Simplification
The circuit can be simplified by combining the three resistors into a single equivalent resistor (Req).
- Equivalent Resistance (Req):Req = R1 + R2 + R3
Numerical Solution, Consider the circuit shown below. find v1 i2 and i3
Assigning numerical values to the circuit components:
- V1 = 12V
- R1 = 2Ω
- R2 = 3Ω
- R3 = 5Ω
Calculating V1, I2, and I3:
- V1 = 12V
- I2 = V1 / (R1 + R2 + R3) = 12V / (2Ω + 3Ω + 5Ω) = 1A
- I3 = I2 = 1A
| Component | Voltage | Current |
|---|---|---|
| R1 | 12V | 1A |
| R2 | 6V | 1A |
| R3 | 3V | 1A |
Discussion
The calculated values indicate that the voltage across each resistor is directly proportional to the resistance value, while the current flowing through each resistor is inversely proportional to the resistance value. This is consistent with Ohm’s law, which states that voltage is directly proportional to current and resistance.
FAQ Resource
What is the significance of V1 in the circuit?
V1 represents the voltage across the resistor R1. It is a crucial parameter that determines the current flow through the resistor and influences the overall voltage distribution within the circuit.
How does the value of R2 affect I2?
The resistance of R2 directly affects the current I2 flowing through it. According to Ohm’s law, a higher resistance value leads to a lower current, and vice versa.