Dichotomous key for leaves answers – Dichotomous Key for Leaves: A Comprehensive Guide to Leaf Identification unveils the fascinating world of leaf identification, empowering you with the knowledge to decipher the intricate tapestry of nature’s verdant kingdom. Embark on a captivating journey through the realm of dichotomous keys, unlocking the secrets of leaf morphology and unlocking the mysteries hidden within their intricate forms.
Delving into the key characteristics that define leaf diversity, we explore the significance of shape, margin, venation, and texture. These fundamental attributes serve as the building blocks of dichotomous keys, enabling us to navigate the labyrinth of leaf variation with precision and confidence.
1. Dichotomous Key for Leaves
Introduction
A dichotomous key is a taxonomic tool that aids in the identification of organisms by dividing them into two contrasting groups based on specific characteristics. In leaf identification, dichotomous keys are employed to systematically classify leaves into different categories based on their observable features.
The significance of dichotomous keys in leaf identification lies in their ability to provide a structured and efficient approach to identifying leaves. By guiding users through a series of questions and choices, dichotomous keys help narrow down the possibilities and lead to the correct identification of the leaf.
Examples of dichotomous keys used for leaf identification include the “Leaf Key” in the “Manual of Woody Plants of North America” by E.L. Little, and the “Key to the Woody Plants of Eastern North America” by E.J. Core and N.L.
Stone.
2. Key Characteristics for Leaf Identification
Dichotomous keys for leaves rely on a set of key characteristics to differentiate between different types of leaves. These characteristics include:
- Leaf Shape:Refers to the overall Artikel or form of the leaf, such as ovate, lanceolate, or palmate.
- Margin:Describes the edge of the leaf, including characteristics such as entire (smooth), serrate (toothed), or lobed.
- Venation:Refers to the pattern of veins on the leaf, including types such as parallel, pinnate, or palmate.
- Texture:Describes the surface texture of the leaf, including characteristics such as smooth, hairy, or scaly.
3. Using a Dichotomous Key: Dichotomous Key For Leaves Answers
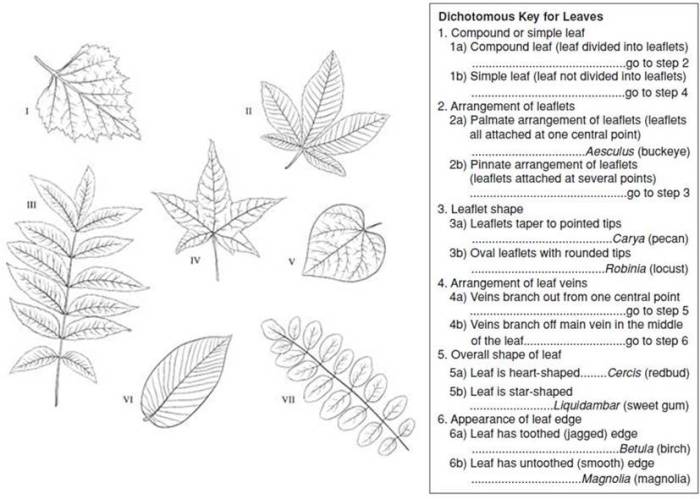
Using a dichotomous key to identify leaves involves following a series of steps:
- Observe the leaf:Examine the leaf and identify its observable characteristics.
- Start at the beginning of the key:Begin at the first question or statement in the key.
- Answer the question or statement:Determine whether the leaf matches the description provided.
- Follow the corresponding lead:If the leaf matches the description, follow the lead that corresponds to the answer.
- Repeat steps 2-4:Continue navigating through the key until you reach a final identification.
4. Applications of Dichotomous Keys

Dichotomous keys for leaves find applications in various fields, including:
- Botany:Used for plant identification and classification.
- Ecology:Applied in vegetation surveys and plant community analysis.
- Forestry:Employed in tree identification and management.
5. Advantages and Limitations
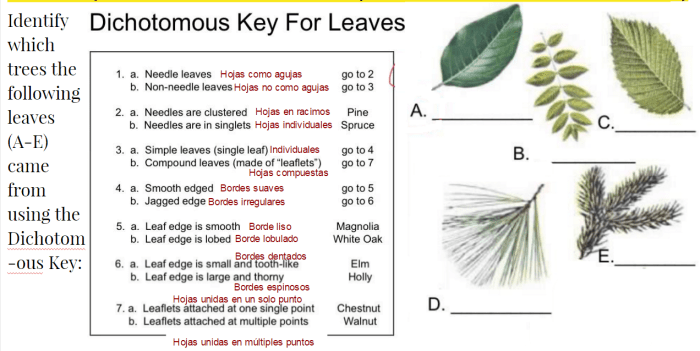
Advantages:, Dichotomous key for leaves answers
- Simplicity:Dichotomous keys are straightforward and easy to use, even for beginners.
- Efficiency:They provide a systematic approach to identification, reducing the time and effort required.
- Accuracy:When used correctly, dichotomous keys can lead to accurate identifications.
Limitations:
- Incomplete Information:Dichotomous keys rely on observable characteristics, which may not always be sufficient for accurate identification.
- Exceptions:Some plants may exhibit variations that do not fit neatly into the key’s categories.
- Subjectivity:The interpretation of leaf characteristics can be subjective, leading to potential errors in identification.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a dichotomous key?
A dichotomous key is a tool used to identify organisms by dividing them into two groups based on a specific characteristic. Each group is then further divided into two subgroups, and so on, until the organism is identified.
How do I use a dichotomous key?
To use a dichotomous key, start at the top of the key and read the first pair of statements. Choose the statement that best describes the organism you are trying to identify, and then follow the arrow to the next pair of statements.
Continue following the arrows until you reach a statement that identifies the organism.
What are the advantages of using a dichotomous key?
Dichotomous keys are a simple and efficient way to identify organisms. They are also relatively easy to use, even for beginners. Additionally, dichotomous keys can be used to identify a wide variety of organisms, including plants, animals, and fungi.